Simulated Annealing is a black-box, derivative-free optimization algorithm
that iterates via stochastic search in the neighborhood of current position.
stiefel.optSA solves the following problem
$$\min_X f(X),\quad X \in St(p,k)$$
without any other auxiliary information such as gradient or hessian involved.
Arguments
- func
a function to be minimized.
- p
dimension parameter as in \(St(k,p)\).
- k
dimension parameter as in \(St(k,p)\).
- ...
extra parameters for SA algorithm including
- n.start
number of runs; algorithm is executed
n.starttimes (default: 5).- stepsize
size of random walk on each component (default: 0.1).
- maxiter
maximum number of iterations for each run (default: 100).
- cooling
triplet for cooling schedule. See the section for the usage.
- init.val
if
NULL, starts from a random point. Otherwise, a Stiefel matrix of size \((p,k)\) should be provided for fixed starting point.- print.progress
a logical; if
TRUE, it prints each iteration.
Value
a named list containing:
- cost
minimized function value.
- solution
a \((p\times k)\) matrix that attains the
cost.- accfreq
frequency of acceptance moves.
Examples
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
# Optimization for Eigen-Decomposition
#
# Given (5x5) covariance matrix S, eigendecomposition is indeed
# an optimization problem cast on the stiefel manifold. Here,
# we are trying to find top 3 eigenvalues and compare.
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
## PREPARE
set.seed(121) # set seed
A = cov(matrix(rnorm(100*5), ncol=5)) # define covariance
myfunc <- function(p){ # cost function to minimize
return(sum(-diag(t(p)%*%A%*%p)))
}
## SOLVE THE OPTIMIZATION PROBLEM
Aout = stiefel.optSA(myfunc, p=5, k=3, n.start=40, maxiter=200)
## COMPUTE EIGENVALUES
# 1. USE SOLUTIONS TO THE ABOVE OPTIMIZATION
abase = Aout$solution
eig3sol = sort(diag(t(abase)%*%A%*%abase), decreasing=TRUE)
# 2. USE BASIC 'EIGEN' FUNCTION
eig3dec = sort(eigen(A)$values, decreasing=TRUE)[1:3]
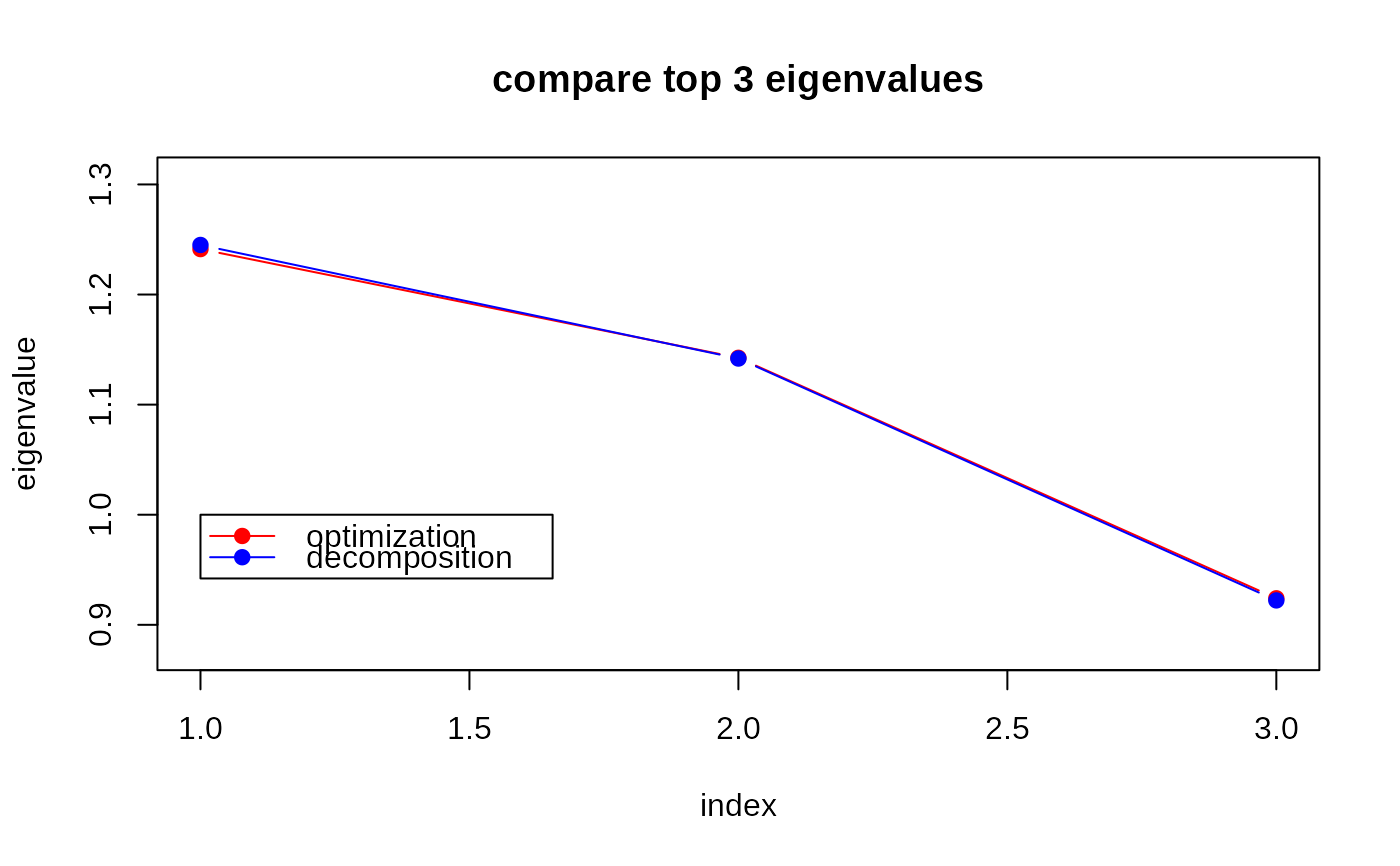
## VISUALIZE
opar <- par(no.readonly=TRUE)
yran = c(min(min(eig3sol),min(eig3dec))*0.95,
max(max(eig3sol),max(eig3dec))*1.05)
plot(1:3, eig3sol, type="b", col="red", pch=19, ylim=yran,
xlab="index", ylab="eigenvalue", main="compare top 3 eigenvalues")
lines(1:3, eig3dec, type="b", col="blue", pch=19)
legend(1, 1, legend=c("optimization","decomposition"), col=c("red","blue"),
lty=rep(1,2), pch=19)
 par(opar)
par(opar)
