This is a collection of tools for learning with spherical Laplace (SL) distribution on a \((p-1)\)-dimensional sphere in \(\mathbf{R}^p\) including sampling, density evaluation, and maximum likelihood estimation of the parameters. The SL distribution is characterized by the following density function, $$f_{SL}(x; \mu, \sigma) = \frac{1}{C(\sigma)} \exp \left( -\frac{d(x,\mu)}{\sigma} \right)$$ for location and scale parameters \(\mu\) and \(\sigma\) respectively.
Usage
dsplaplace(data, mu, sigma, log = FALSE)
rsplaplace(n, mu, sigma)
mle.splaplace(data, method = c("DE", "Optimize", "Newton"), ...)Arguments
- data
data vectors in form of either an \((n\times p)\) matrix or a length-\(n\) list. See
wrap.spherefor descriptions on supported input types.- mu
a length-\(p\) unit-norm vector of location.
- sigma
a scale parameter that is positive.
- log
a logical;
TRUEto return log-density,FALSEfor densities without logarithm applied.- n
the number of samples to be generated.
- method
an algorithm name for concentration parameter estimation. It should be one of
"Newton","Optimize", and"DE"(case-sensitive).- ...
extra parameters for computations, including
- maxiter
maximum number of iterations to be run (default:50).
- eps
tolerance level for stopping criterion (default: 1e-6).
- use.exact
a logical to use exact (
TRUE) or approximate (FALSE) updating rules (default:FALSE).
Value
dsplaplace gives a vector of evaluated densities given samples. rsplaplace generates
unit-norm vectors in \(\mathbf{R}^p\) wrapped in a list. mle.splaplace computes MLEs and returns a list
containing estimates of location (mu) and scale (sigma) parameters.
Examples
# \donttest{
# -------------------------------------------------------------------
# Example with Spherical Laplace Distribution
#
# Given a fixed set of parameters, generate samples and acquire MLEs.
# Especially, we will see the evolution of estimation accuracy.
# -------------------------------------------------------------------
## DEFAULT PARAMETERS
true.mu = c(1,0,0,0,0)
true.sig = 1
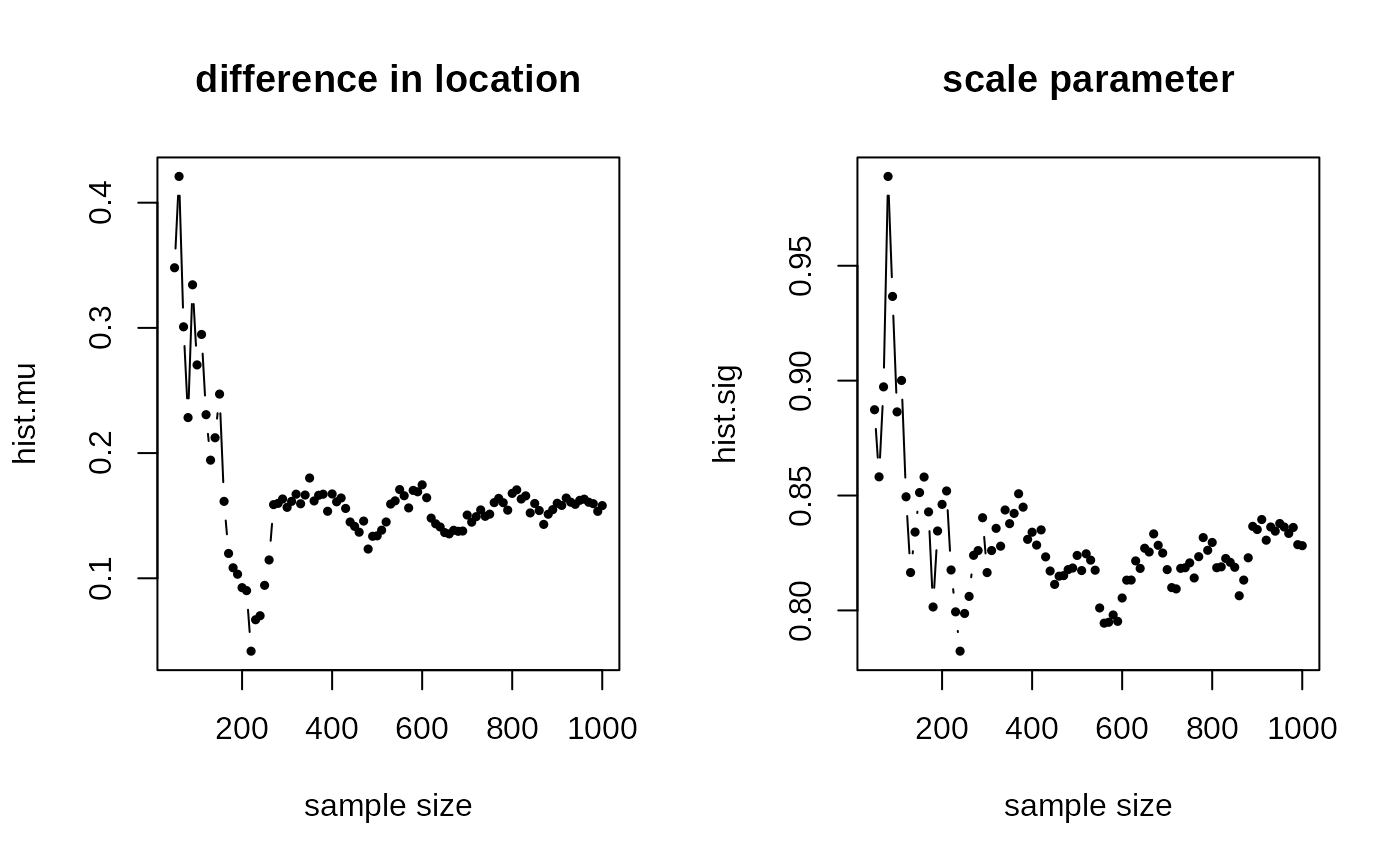
## GENERATE A RANDOM SAMPLE OF SIZE N=1000
big.data = rsplaplace(1000, true.mu, true.sig)
## ITERATE FROM 50 TO 1000 by 10
idseq = seq(from=50, to=1000, by=10)
nseq = length(idseq)
hist.mu = rep(0, nseq)
hist.sig = rep(0, nseq)
for (i in 1:nseq){
small.data = big.data[1:idseq[i]] # data subsetting
small.MLE = mle.splaplace(small.data) # compute MLE
hist.mu[i] = acos(sum(small.MLE$mu*true.mu)) # difference in mu
hist.sig[i] = small.MLE$sigma
}
## VISUALIZE
opar <- par(no.readonly=TRUE)
par(mfrow=c(1,2))
plot(idseq, hist.mu, "b", pch=19, cex=0.5,
main="difference in location", xlab="sample size")
plot(idseq, hist.sig, "b", pch=19, cex=0.5,
main="scale parameter", xlab="sample size")
abline(h=true.sig, lwd=2, col="red")
 par(opar)
# }
par(opar)
# }
